Subsections of Virtual machines
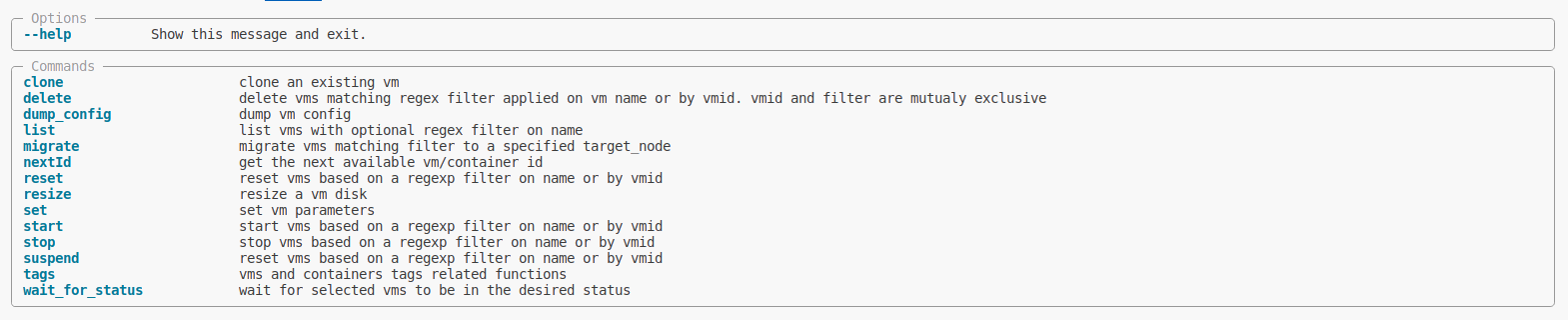
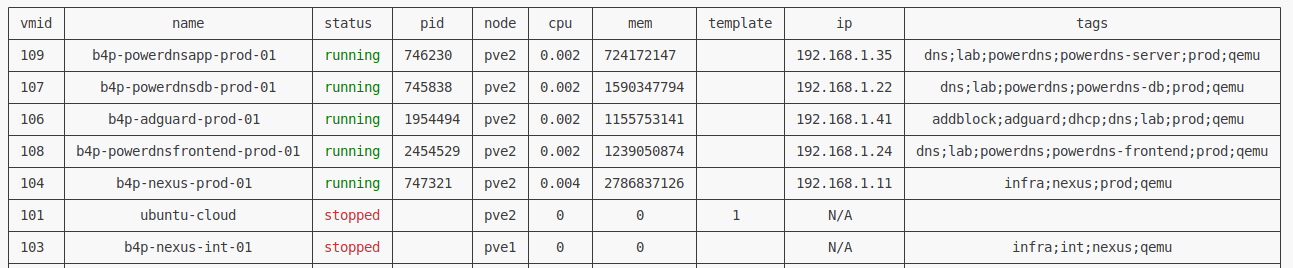
List virtual machines
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| filter-name | apply a regex filter on virtual machines name | regex string |
| output-format | output the result of the list command in the selected format (default to table) | table or yaml or json |
| proxmox-node | coma separated list of proxmox nodes where we will search for virtual machines | node1,node2,node3 |
| status | virtual machine status | running or stopped |
Examples
- This command will output an unfiltered list of virtual machines available on the cluster
proxcli vms list- This command will output a list of virtual machines on selected nodes
proxcli vms list --proxmox-nodes pve1,pve2- This commands will output a list of virtual machines filterd by a regular expression applied on virtual machine name
proxcli vms list --filter-name "^b4p-"- This command will output a list of virtual machines with the specified status (comma separated list possible)
proxcli vms list --status running- You can combine the different filters together. This command show running vms matching a filter on virtual machine name on a specified node
proxcli vms list --status running --proxmox-node pve2 --filter-name ".*powerdns.*"output formating
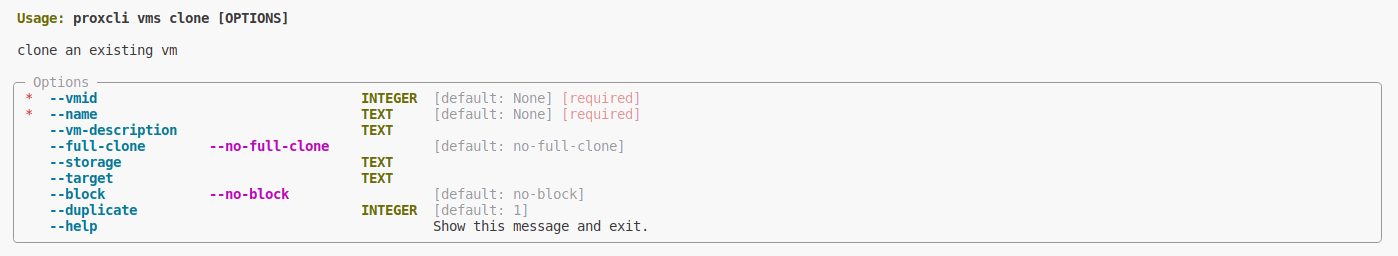
Clone a virtual machine template
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vmid | virtual machine template id to be cloned | integer |
| name | virtual machine clone name | regex string |
| vm-description | virtual machine clone description | string |
| full-clone | A full clone VM is a complete copy and is fully independant to the original VM or VM Template, but requires the same disk space as the original. | N/A |
| storage | storage name (local or remote) where the virtual machine disk image will be cloned | string |
| target | the target proxmox node name where the cloned virtual machine will be assigned | string |
| block | will the clone process will block until it end ? It make sense on slow remote storage (like on NAS), we wait for the clone task to finish before doing the next clone. This prevent IO saturation on storage | N/A |
| duplicate | how many duplicate do we need ? each duplicate will get his name suffixed by an index. | integer |
vmid and name are mutualy exclusive
Examples
- Clone a virtual machine template
proxcli vms clone --vmid 111 --name test --vm-description test --full-clone --block --target pve2 --storage b4papp - Clone a virtual machine template with cloud enabled template
This is the same command as for a normal clone but you need additional steps to set user, password, ssh public key and network configuration. Try the following commands after cloning finishes.
proxcli vms set --vmid 112 --ciuser myuser --cipassword mypassword --ipconfig "ip=dhcp" --sshkey "$(cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)"
proxcli vms set --vmid 112 --cores 4 --memory 4096
proxcli vms resize --vmid 112 --disk virtio0 --size "50G"Make sure you already have a cloud init enabled template on your proxmox nodes. You can find in the next section an example of creating an ubuntu server cloud init enabled image.
you will need virt-customize tool on your proxmox nodes in order to install qemu-guest-agent (install it with apt install libguestfs-tools) you also need an ubuntu cloud-init enabled image. You can find one here
virt-customize -a lunar-server-cloudimg-amd64.img --install qemu-guest-agent
virt-customize -a lunar-server-cloudimg-amd64.img --run-command "echo -n > /etc/machine-id"Those commands will help you create an ubuntu cloud init enabled virtual machine template. Adjust the variables at the begining of the script so it match your needs.
vmid=$(pvesh get /cluster/nextid)
isopath="/mnt/pve/isos/template/iso/lunar-server-cloudimg-amd64.img"
templatename="lunar-server-cloudinit"
memory=2048
storage="b4papp"
scsihw="virtio-scsi-pci"
devname="virtio"
disksize="5G"
qm create $vmid --memory ${memory} --name ${templatename} --net0 virtio,bridge=vmbr0
qm set $vmid --agent enabled=1
qm importdisk $vmid $isopath $storage
qm set $vmid --scsihw $scsihw --${devname}0 ${storage}:${vmid}/vm-${vmid}-disk-0.raw
qm set $vmid --ide2 ${storage}:cloudinit
qm set $vmid --boot c --bootdisk ${devname}0
qm resize $vmid ${devname}0 ${disksize}
qm set ${vmid} --serial0 socket --vga serial0
qm template ${vmid}On some shared storages (like Synology NFS share), you may encounter the following error with qm template command:
/usr/bin/chattr: Operation not supported while reading flags on /mnt/pve/b4papp/images/111/base-111-disk-0.rawYou don’t have to do anything, it is just a limitation in synology hardening. But it does not affect the creation of a template.
Set virtual machine parameters
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vmid | The (unique) ID of the VM. | integer |
| vmname | Virtual Machine exact name | string |
| cores | The number of cores per socket. | integer |
| sockets | The number of CPU sockets. | integer |
| cpulimit | Limit of CPU usage. NOTE: If the computer has 2 CPUs, it has total of ‘2’ CPU time. Value ‘0’ indicates no CPU limit. | integer |
| memory | Amount of RAM for the VM in MiB. This is the maximum available memory when you use the balloon device. | integer |
| ipconfig | cloud-init: Specify IP addresses and gateways for the corresponding interface. IP addresses use CIDR notation, gateways are optional but need an IP of the same type specified. The special string ‘dhcp’ can be used for IP addresses to use DHCP, in which case no explicit gateway should be provided. For IPv6 the special string ‘auto’ can be used to use stateless autoconfiguration. This requires cloud-init 19.4 or newer. If cloud-init is enabled and neither an IPv4 nor an IPv6 address is specified, it defaults to using dhcp on IPv4. | string |
| cipassword | cloud-init: Password to assign the user. Using this is generally not recommended. Use ssh keys instead. Also note that older cloud-init versions do not support hashed passwords. | string |
| ciuser | cloud-init: User name to change ssh keys and password for instead of the image’s configured default user. | string |
| citype | Specifies the cloud-init configuration format. The default depends on the configured operating system type ostype. We use the nocloud format for Linux, and configdrive2 for windows. | string |
| boot | Specify guest boot order. Use the ‘order=’ sub-property as usage with no key or ’legacy=’ is deprecated. | string |
| sshkey | cloud-init: Setup public SSH key | string |
Set parameters is a small subset of what is available in the proxmox API. I (maybe) will had more parameters later.
Examples
assert we have already cloned a cloud init enabled ubuntu virtual machine with the following command:
proxcli vms clone --vmid 100 --full-clone --block --name ubuntu-cloud-init-clone --vm-description exemple_clone --target pve1 --storage b4pappthe cloned vm is not started yet
- cloud init configuration of a vm cloned from a cloud init enabled ubuntu virtual machine
proxcli vms set --vmid 110 --ciuser myuser --cipassword mypassword --ipconfig "ip=dhcp" --sshkey "$(cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)"- adjust resources of a cloned virtual machine
proxcli vms set --vmid 110 --cores 4 --memory 4096- start the cloned virtual machine
proxcli vms start --vmid 111Resize virtual machine disk
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vmid | the virtual machine id from which you want to resize the disk | string |
| vmname | the virtual machine name from which you want to resize the disk | string |
| filter-name | regex selector applied on virtual machines names you want to resize the disk | string |
| disk | the disk name in virtual machine config (usualy the one associated with bootdisk) | string |
| size | The desired size of the disk (Ex: 50G) | string |
vmid, vmname and filter-name are mutualy exclusive
Examples
- resize the boot disk
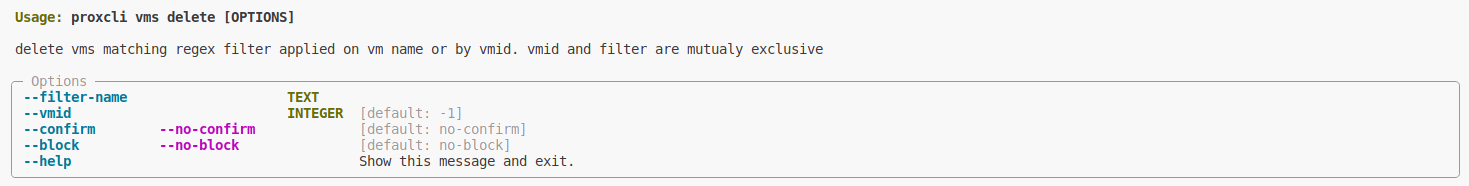
proxcli vms resize --vmid 111 --disk virtio0 --size "60G"Delete virtual machine
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vmid | the virtual machine id you want to delete | string |
| filter-name | a regex applied on virtual machine name | string |
| confirm | does not ask for confirmation | N/A |
| block | block the command until it finished | N/A |
Examples
- delete a virtual machine by its id
proxcli vms delete --vmid 111- delete all virtual machines matching the specified regex
proxcli vms delete --filter-name "^b4p"- delete all virtual machines matching the specified regex without any confirmation and wait for all deletion to be finished before exiting
proxcli vms delete --filter-name "^b4p" --confirm --blockDump virtual machine config
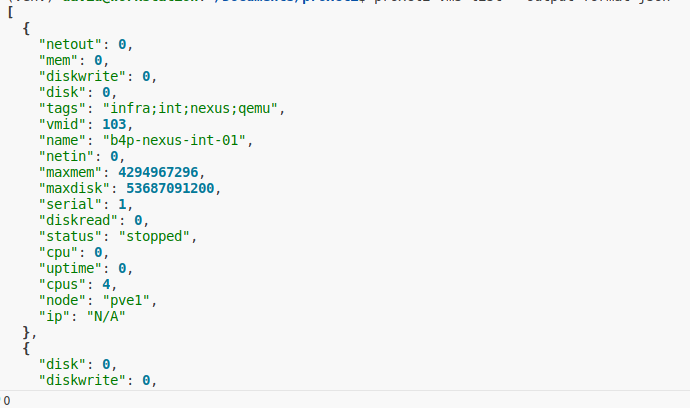
Arguments
| argument | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vmid | virtual machine from which we want to dump the config | integer |
Examples
- dump config of a virtual machine
proxcli vms dump_config 111Migrate a virtual machine
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vmid | The virtual machine id to migrate | integer |
| filter-name | A regex string to select multiple virtual machines to be migrated | string regex |
| target-node | the proxmox target node name | string |
vmid and filter-name are mutualy exclusive
Examples
You can’t migrate a running virtual machine. The only way to do live migration is through cluster ha resource migrate. See cluster ha section
- migrate a virtual machine from one proxmox node to other
proxcli vms migrate --vmid 111 --target-node pve2 - migrate multiples virtual machines by selecting the with a regex filter on their name
proxcli vms migrate --filter-name "^b4p" --target-node pve2Display the next available vm id
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|
Examples
- Display the next available virtual machine id
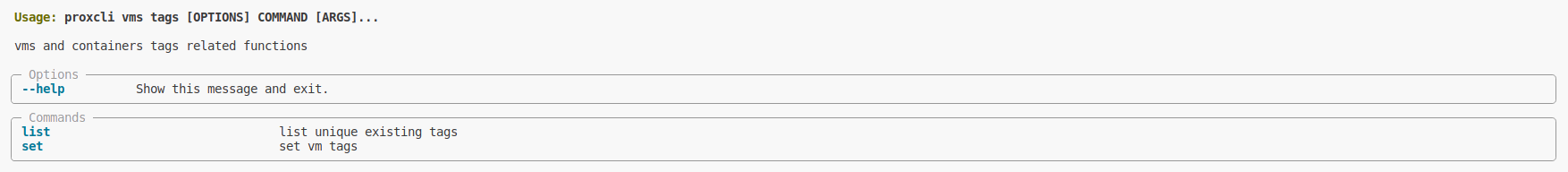
proxcli vms nextIdvirtual machine tags
Subsections of virtual machine tags
List virtual machine tags
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|
Examples
- list all virtual machine tags
proxcli vms tags listSet virtual machine tags
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vm-tags | coma separated list of tags | string |
| filter-name | regex applied to match virtual machine names | string |
| set-mode | whether we can append or replace tags. default to replace | string |
Examples
- Set tags for all vms name matching the specified regex
proxcli vms tags set --vm-tags "template,ubuntu" --filter-name "^ubuntu-cloud"- append tags for all vms name matching the specified regex
proxcli vms tags set --vm-tags "newtag" --filter-name "^ubuntu-cloud" --set-mode appendSet virtual machine status
Description
Virtual machine status commands use the same options interface for every desired status. The following options table apply to all status commands such as start, stop, suspend or reset.
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vmid | the virtual machine id you want to delete | string |
| filter-name | a regex applied on virtual machine name | string |
Examples
- Start virtual machine
proxcli vms start --vmid 101- Stop virtual machine
proxcli vms stop --vmid 101- Suspend all virtual machines with name matching specified regex
proxcli vms suspend --filter-name "^b4p"- Reset virtual machine
proxcli vms reset --vmid 101Wait for virtual machine status
Description
wait for virtual machines to reach the desired status (stopped, running …)
Options
| option | description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| vmid | the virtual machine id you want to wait for reaching the desired status | string |
| name | the virtual machine name you want to wait for reaching the desired status | string |
| filter-name | a regex applied on virtual machine name you want to wait for reaching the desired status | string |
| status | the desired status | string |
vmid, name and filter-name are mutualy exclusive
Examples
- wait for every virtual machine with name start with test to be stopped
proxcli vms wait_for_status --filter-name "^test" --status "stopped"